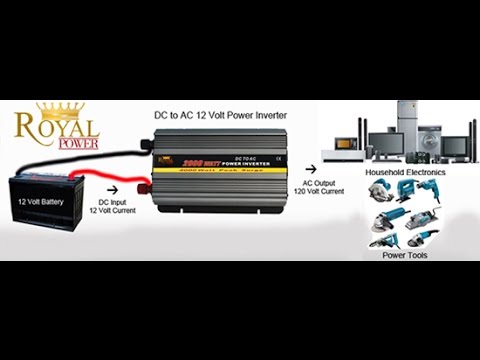
A power inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It allows the use of AC-powered devices with a DC power source.
Power inverters are crucial for converting DC from batteries, solar panels, or other sources into AC. This enables the operation of household appliances, tools, and electronic devices when traditional power sources are unavailable. These devices are essential for off-grid living, RVs, and emergency power backup.
They come in various types, such as pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters, each suited to different needs. Choosing the right inverter depends on the power requirements and the type of devices you intend to use. Proper selection ensures efficient energy use and device safety.

Credit: theengineeringmindset.com
Introduction To Power Inverters
A power inverter changes direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This lets you use devices that need AC power from DC sources. DC sources include car batteries or solar panels. Inverters are very useful. They make sure you can power your home or appliances. They keep important devices running during power cuts.
Power inverters are used in many ways. They power home appliances and electronic devices. You can use them in RVs and boats. They are essential for solar power systems. Inverters also help in emergency situations. They keep medical devices running when there is no power. Inverters are very helpful and useful in daily life.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Basic Components
The inverter unit changes DC power to AC power. This is crucial for most home appliances. The unit contains circuits and switches. These parts help in the conversion process. Inverter units come in different sizes. Some are small for gadgets. Others are large for homes.
Batteries store energy for the inverter. They provide the DC power needed. Car batteries or solar batteries can be used. The battery capacity is important. Bigger batteries store more energy. This means longer use time. Battery types vary based on needs.
Types Of Power Inverters
Sine wave inverters produce a smooth and clean wave. They are ideal for sensitive electronics. Most household appliances prefer sine wave power. Computers, TVs, and microwaves work better with sine wave. Sine wave inverters are more expensive but efficient. They can handle heavy loads without trouble.
Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper. They produce a less smooth wave. Some devices may buzz or not work well. They are good for simple tools. Fans and lights work fine with them. Modified sine wave inverters are less efficient. They might not handle heavy loads well.
Credit: www.matsusada.com
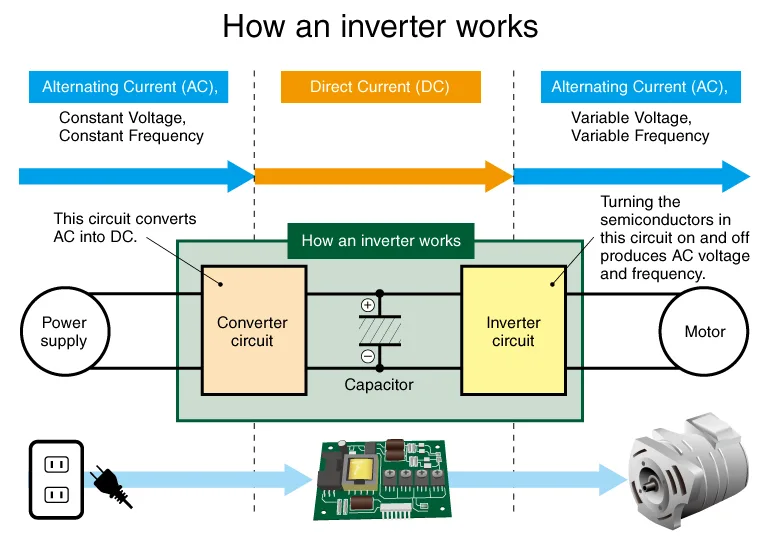
How Power Inverters Work
Power inverters convert Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC). They are crucial for devices that need AC power. Batteries and solar panels produce DC power. Most home appliances require AC power. The inverter bridges this gap by converting DC to AC.
The inversion process starts with a DC input. This input comes from a battery or solar panel. The inverter then uses electronic circuits to switch the DC to AC. These circuits create an AC waveform. The waveform can be a sine wave, modified sine wave, or square wave. Sine waves are the best for sensitive devices. Modified sine waves work for most household items. Square waves are the least efficient but cheapest.
Key Features
A power inverter changes DC power to AC power. This process is very efficient. Most inverters have an efficiency of 85% to 95%. This means less energy is wasted. High efficiency is important for saving energy. It also helps in reducing costs.
Power inverters come in different sizes. They can provide various levels of power output. Some inverters can power small devices. Others can run large appliances. It’s important to choose the right size. A higher power output is needed for bigger devices. This ensures everything runs smoothly.
Choosing The Right Inverter
Understanding load requirements is crucial. Calculate the total wattage of devices to be powered. Add a safety margin of 20% to the total wattage. This ensures the inverter can handle power surges. Choose an inverter that matches or exceeds this wattage.
Temperature affects inverter performance. High temperatures can cause overheating. Ensure proper ventilation. Humidity can cause short circuits. Choose an inverter with protection features. Dust can clog the inverter, affecting efficiency. Install the inverter in a clean, dry place.
Installation And Maintenance
Always wear protective gear while working with power inverters. Ensure the inverter is off before touching any wires. Make sure the area is dry to avoid electric shocks. Use insulated tools to prevent any accidents. Keep flammable materials away from the inverter. Ensure the inverter is properly grounded. Check for damaged wires and replace them immediately.
Inspect the inverter’s connections every month. Look for loose or corroded wires. Clean the ventilation areas to prevent overheating. Test the output voltage regularly. Ensure the battery connections are tight. Check for any unusual noises from the inverter. Verify the cooling fan is working properly.
Common Issues And Troubleshooting
Overload happens if too many devices connect to the inverter. The inverter may shut down to protect itself. Reduce the number of connected devices to solve this. Always check the power rating of your inverter. This ensures you do not exceed its capacity. Use devices within the inverter’s wattage limit.
Weak or dead batteries cause inverter problems. Check the battery voltage regularly. Ensure the connections are tight and clean. Charge the batteries fully before use. Replace old batteries if they can’t hold a charge. Proper battery maintenance ensures a longer life for the inverter.
Future Trends
Power inverters are becoming more efficient and compact. New materials help reduce power loss and improve performance. Smart inverters can now connect to the internet. They can be controlled remotely with mobile apps. Some models even use artificial intelligence to optimize energy use.
The demand for power inverters is rising. More people are using solar panels and electric vehicles. These technologies need efficient power inverters. The market is expected to grow rapidly in the next few years. Many companies are investing in new inverter technologies. This will likely lead to more advanced and affordable products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Power Inverter Used For?
A power inverter converts DC power from a battery into AC power. This allows you to run AC devices using a DC power source. It’s useful for camping, RVs, and emergency backups.
How Does A Power Inverter Work?
A power inverter uses electronic circuits to change DC power into AC power. It modifies the voltage and current to match household appliances. The process involves oscillators, transformers, and rectifiers.
Can A Power Inverter Power A House?
Yes, a power inverter can power a house for short periods. It’s ideal for emergency situations or off-grid living. The power source is typically a battery or solar panels.
What Types Of Power Inverters Are There?
There are two main types of power inverters: pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverters are more efficient and suitable for sensitive electronics. Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but less efficient.
Conclusion
Understanding power inverters is essential for modern energy solutions. They convert DC to AC, powering various devices efficiently. Whether for home use or travel, they offer versatility and convenience. Choose the right inverter to meet your energy needs and enjoy seamless power supply wherever you go.