Choosing the right inverter wattage can feel confusing, but it’s one of the most important steps to ensure your power needs are met without wasting money or risking damage. Whether you’re setting up a solar system, preparing for emergencies, or simply want reliable backup power, knowing how to size your inverter correctly makes all the difference.
In this guide, you’ll learn easy-to-follow steps to calculate your power needs, understand surge versus running watts, and pick an inverter that matches your lifestyle perfectly. By the end, you’ll feel confident in making a smart choice that keeps your devices running smoothly and your energy system efficient.
Let’s get started on finding the right inverter size for you!
Calculating Inverter Wattage
Choosing the correct inverter wattage starts with calculating your power needs. This step ensures your inverter runs efficiently and safely. Accurate calculations prevent overload and extend the life of your system.
Break down your power requirements by considering every appliance you plan to use. Include devices that will operate at the same time to get a clear picture of your load. This process helps find the right size inverter for your setup.
List Appliances And Wattage
Make a detailed list of all appliances you want to power. Check each device’s label for its wattage rating. Use a watt meter for exact measurements if labels are unclear. Include small and large items to avoid underestimation.
Identify Surge Wattage
Some appliances need extra power when starting. This is called surge wattage or peak load. Common devices with surge include refrigerators and air conditioners. Note these higher values to ensure your inverter can handle startup demands.
Calculate Total Running Load
Add the continuous wattage of all appliances that will run at once. This total is your running load. Use this figure to determine the basic power your inverter must supply steadily. Do not forget to include lights, fans, and electronics.
Calculate Peak Load
Identify the largest single surge wattage from your appliances. Add this to your total running load. The result is the peak load your inverter must support. This step avoids inverter overload during device startups.
Add Safety Margin
Include a safety margin of 20-25% to your peak load calculation. This extra capacity protects your inverter from unexpected power spikes. It also accounts for future appliances or changes in power use. Choose an inverter rated above this final number.
Selecting Inverter Specifications

Choosing the right inverter starts with understanding its key specifications. These specs ensure your inverter meets your power needs safely and efficiently. Knowing the continuous rating, surge rating, and compatibility helps you select the best inverter. This section explains these important factors.
Continuous Rating
The continuous rating shows how much power the inverter can supply nonstop. It is measured in watts. This rating must cover all devices you run at the same time. Pick an inverter with a continuous rating above your total power needs. This prevents overloading and ensures smooth operation.
Surge Rating
The surge rating is the maximum power the inverter can handle briefly. Some appliances need extra power to start, called surge power. This rating should be higher than the highest startup power of your devices. A good surge rating keeps the inverter safe during these power spikes.
Compatibility With Battery And Panels
The inverter must work well with your battery and solar panels. Check the voltage and current ratings to match your system. A mismatch can cause poor performance or damage. Choose an inverter designed for your battery type and panel output. This keeps your system efficient and reliable.
Read More: How To Make Power Inverter 12V to 220V at Home
Common Inverter Sizes
Choosing the right inverter size starts with understanding common inverter wattage options. Inverters come in various sizes to fit different power needs. Knowing these sizes helps you pick an inverter that matches your energy use. This prevents overloading and ensures efficient power supply. Below are typical inverter sizes used in homes.
Small Residential Inverters
Small inverters usually range from 300 to 1000 watts. They are ideal for basic needs like charging phones and running small lights. These inverters work well in tiny homes or cabins. They support low power devices without wasting energy or money.
Medium Home Systems
Medium-sized inverters range between 1000 and 3000 watts. They can power multiple appliances like TVs, fans, and refrigerators. These inverters suit most average homes with moderate electricity use. They offer a balance of power and cost efficiency.
Large Capacity Inverters
Large inverters exceed 3000 watts and can handle heavy power loads. They support many appliances running at once, including air conditioners and water pumps. These inverters are best for big homes or small businesses. They ensure stable power even during high demand.
Inverter Sizing Examples
Understanding inverter sizing can seem tricky. Examples help clarify how to pick the right wattage. Each setup needs a different size inverter based on power use and device type. Below are practical inverter sizing examples for common scenarios.
Basic Home Setup
A typical home uses appliances like lights, TV, and fridge. Add their wattages: lights 300W, TV 150W, fridge 700W.
Total running load is 1150 watts. The fridge has a surge wattage of 2100W due to startup.
Choose an inverter with at least 1150W continuous and 2100W surge capacity. A 2000W inverter often works well here.
Rv And Mobile Applications
RVs need power for small devices: laptop 60W, mini fridge 100W, lights 50W.
Total running load equals 210 watts. Surge wattage might reach 300W for the fridge.
A 400W inverter covers these needs with some safety margin. Compact size fits mobile use.
Off-grid Solar Systems
Off-grid homes rely on solar and batteries. Appliances include lights 200W, water pump 500W, and TV 150W.
Total running load is 850 watts. Water pump surge wattage can be 1500W.
Select an inverter of at least 1000W continuous and 1500W surge. This ensures reliable power from solar.
Read More: What Will a 1000 Watt Power Inverter Run?
Factors Affecting Inverter Choice
Choosing the right inverter wattage depends on several important factors. Understanding these will help you pick an inverter that meets your power needs efficiently. The size must match the type of appliances, how many run at once, and other key considerations.
Type Of Appliances
Different appliances consume different amounts of power. Small devices like LED bulbs need less wattage. Larger appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners require more power. Knowing the wattage of each appliance helps you choose the correct inverter size.
Simultaneous Usage
Many devices might run at the same time. The inverter must handle the total power of all running appliances together. Add the wattage of each device that operates simultaneously to find the total load. This total guides the minimum inverter capacity needed.
Surge Needs Of Motors
Motors in devices like fans and pumps draw extra power at startup. This surge can be two to three times the running wattage. The inverter must support this surge without damage. Consider surge wattage when sizing your inverter to avoid overload.
Future Expansion
Plan for more appliances in the future. Choosing a slightly larger inverter allows for new devices without replacing the inverter. This saves cost and hassle later. Always leave room for growth in your power needs.
Tips For Efficient Inverter Use
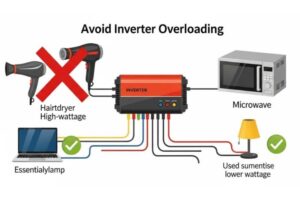
Using an inverter efficiently extends its life and improves performance. Simple steps keep your system safe and reliable. Follow these tips to get the most from your inverter.
Avoiding Overloading
Do not connect devices that exceed the inverter’s wattage limit. Overloading causes damage and shuts down your system. Check each appliance’s wattage before use. Run only essential devices at the same time. This keeps the inverter within safe limits.
Maintaining Safety Margins
Choose an inverter with a wattage rating higher than your total load. A 20-30% safety margin prevents unexpected shutdowns. It also handles power surges from appliances like refrigerators or pumps. This margin protects your investment and ensures stable power supply.
Regular Maintenance
Clean the inverter and its vents often to avoid overheating. Dust and dirt reduce cooling efficiency and cause failures. Inspect connections and cables for wear or corrosion. Tighten loose connections to prevent power loss. Schedule checks every few months to keep the inverter in top shape.
Conclusion
Choosing the right inverter size protects your devices and saves energy. Start by listing all appliances you want to power at once. Add their running watts and include the highest surge wattage. Always pick an inverter with ratings above your total needs.
This approach ensures smooth operation without overloads. Proper sizing helps your system run efficiently and lasts longer. Keep these simple steps in mind for a reliable power setup.

