A power inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for powering electrical devices. It allows batteries to run AC appliances anywhere.
Power inverters serve as a pivotal gadget bridging the gap between limited DC power sources, such as batteries, and the vast array of AC appliances we use daily. By transforming DC from vehicles or renewable energy sources into AC, inverters make it possible to use traditional electronics off-the-grid or while on the move.
They are essential for camping trips, remote job sites, and emergency backup power, offering versatility in how and where we use our devices. From charging a laptop to running a fridge, inverters ensure we stay connected and comfortable, independent of a fixed power supply. Whether for convenience or necessity, a power inverter turns stored energy into practical power, fostering greater autonomy in our electricity-dependent world.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Introduction To Power Inverters
A power inverter is a device that transforms direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion allows the use of household electronics in environments where only DC power is available. Often found in cars and solar power systems, inverters enable the operation of devices outside traditional settings.
The core purpose of these devices is to offer flexibility in power usage. For example, people can charge laptops or use other electronics during car trips. Inverters also play a significant role in areas with unreliable electricity.
The concept of power inversion has a rich history, advancing from basic designs to complex, high-efficiency units. Early inverters were simple, bulky, and not particularly efficient. Over time, technological advancement has led to compact, powerful, and reliable inverter designs.

Credit: www.schumacherelectric.com
Types Of Power Inverters
Power inverters change DC power to AC power. People use them to run electrical devices in cars, boats, or when camping. They are handy during power outages too. There are three main types of inverters: Square Wave, Modified Sine Wave, and Pure Sine Wave. Each type suits different needs.
Square Wave inverters are the most basic and least expensive. They work well with simple tools but not with sensitive electronics. Modified Sine Wave inverters work with most devices, giving a balance between price and function. For the best performance, especially for medical equipment and high-end electronics, Pure Sine Wave inverters are preferred. They mimic the power from an outlet.
| Inverter Type | Good For | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Square Wave | Simple tools | Least Expensive |
| Modified Sine Wave | Most devices | Moderate |
| Pure Sine Wave | High-end electronics | Most Expensive |
Selecting the right inverter needs careful thought. Consider the type of devices you want to power. Think about inverter capacity and power output. Cost, efficiency, and safety features matter too. Checking the compatibility with your devices is essential.
Common Uses Of Power Inverters
Power inverters change DC power into AC power. Homes often use these for running appliances during blackouts. Devices like laptops and microwaves get power this way. People also use inverters outdoors. They power tools and lights at places with no electricity.
In businesses, these inverters support machines and computers. They keep work going if power cuts happen. Important for hospitals, they help emergency equipment work all the time.
- For fun outside, inverters run speakers or chargers.
- Campers use inverters to make camping trips better.
Backup power comes from inverters too. During emergencies, they are like lifelines. Lights and phones can stay on. This helps people stay safe and in touch.
Inverters are key in solar power systems. They let homes use clean energy. Solar panels make DC power. Inverters change it to AC. This lets people run TVs and fridges on solar power.
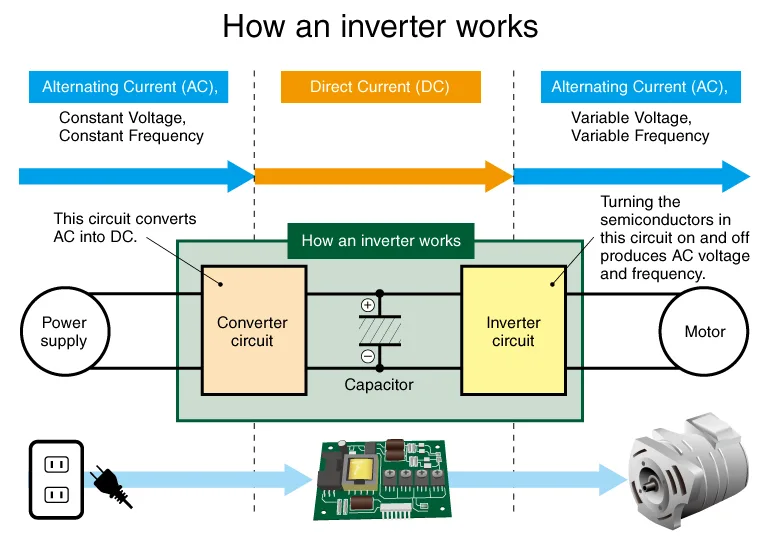
Credit: www.matsusada.com
Technical Considerations
Power inverters convert DC (Direct Current) electricity to AC (Alternating Current). Voltage and wattage are key in power ratings and capacity. A 1000-watt inverter can run items within that power limit.
Efficiency means how well the inverter turns DC into AC. A higher efficiency equals less energy lost as heat. 80% efficiency or more is good. With power loss, a 1000W inverter might only give 800W after efficiency losses.
Safety features in inverters keep us and our gadgets safe. Look for overload protection, temperature control, and short-circuit prevention. Good protections make a power inverter reliable and long-lasting.
Buying And Installation Tips
Identifying your power requirements is crucial for choosing a power inverter. Start by listing all the devices you plan to power. Note their wattage to calculate total power needs. This ensures the inverter can handle the load.
For choosing the right type of power inverter, understand the different types available. Pure sine wave inverters suit sensitive electronics, while modified sine wave inverters work for simpler tools. Peak power rating and continuous power define an inverter’s capacity. Choose an inverter with a continuous rating above your total power needs.
Installation best practices include securing the inverter near the battery. This minimizes voltage drop. Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating. Always use recommended gauge wiring and follow the manufacturer’s guide. Ground the inverter properly for safety. A professional installation is advised for complex setups.
Maintenance And Troubleshooting
Maintenance of a power inverter ensures long-term performance. Regularly check connections for corrosion. Clean them with a simple mixture of baking soda and water. Ensure the inverter’s fan is free of dust, as overheating can cause issues.
Power inverters can fail due to myriad issues. Overloading the inverter frequently leads to performance drops. Confirm load doesn’t surpass inverter’s output capacity. For unresponsive inverters, a soft reset often works. Check fuses and replace if blown. Consult the manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Consider an upgrade when performance consistently dips. Newer models offer improved efficiency and additional features. Compare continuous and peak power output with your requirements before upgrading. Seek professional advice to select an appropriate model for your needs. Installing a higher capacity might prove beneficial for expanding usage.
The Future Of Power Inverters
Power inverters are undergoing significant improvements, shaping a future where energy conversion is more efficient and reliable. Key enhancements include higher conversion efficiencies and the integration of smart technologies.
These advancements position inverters as pivotal components within smart grids. Smart grids use inverters to balance and distribute energy from renewable sources. As a result, efficiency in energy usage sees substantial gains.
Looking ahead, market experts anticipate a rise in the demand for advanced inverters. This is driven by the increasing adoption of solar panels and electric vehicles. The emerging trends suggest a bright outlook for the inverter industry, with potential for new applications and growth.
Conclusion
Power inverters are indispensable in transforming DC to AC power, catering to various needs, from road trip conveniences to vital support in power outages. They empower us to use our favorite devices anywhere, making them a versatile tool for work and leisure alike.
Embracing this technology enhances our daily lives, reaffirming the inverter’s place in modern setups.

