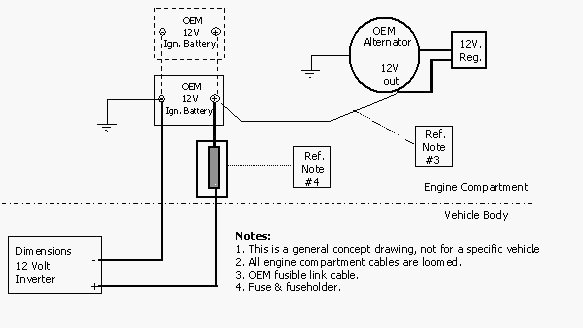
How to Install a Power Inverter in a Car?
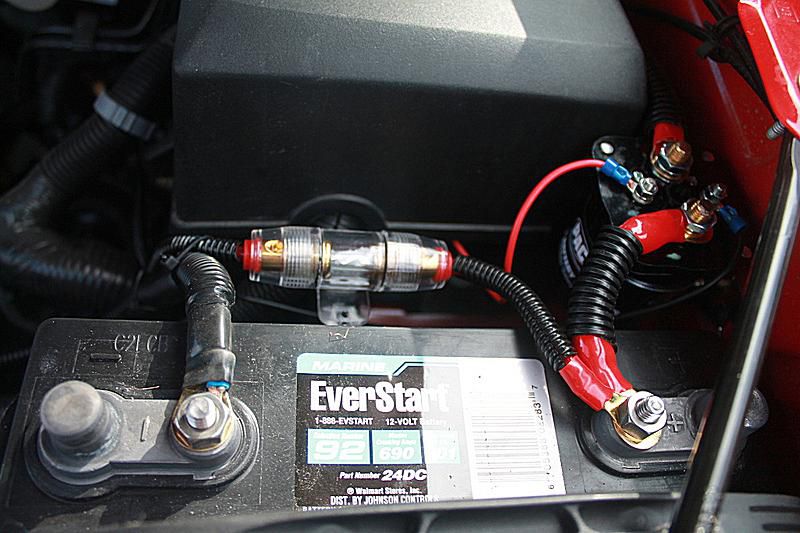
To install a power inverter in a car, connect it to the battery and secure it to a stable surface. Ensure the inverter is off and the car battery is disconnected before installation. Installing a power inverter in a vehicle transforms it into a mobile power hub, allowing the use of household electronics on the … Read more